The territory of the former East Germany (divided into five new Länder in 1990) accounts for almost one-third of united Germany’s territory and one-fifth of its population. After a close vote, in 1993 the Bundestag, the lower house of Germany’s parliament, voted to transfer the capital from Bonn in the west to Berlin, a city-state in the east surrounded by the Land of Brandenburg.
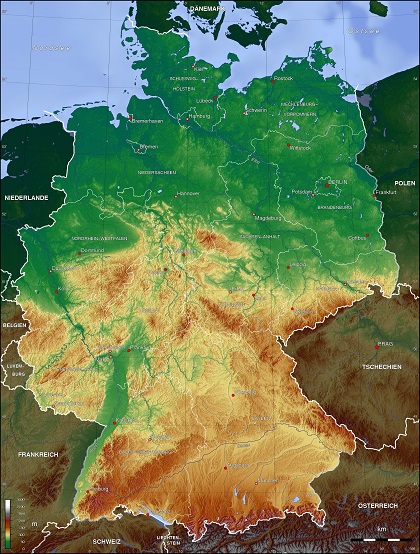
Topography: With its irregular, elongated shape, Germany provides an excellent example of a recurring sequence of landforms found the world over. A plain dotted with lakes, moors, marshes, and heaths retreats from the sea and reaches inland, where it becomes a landscape of hills crisscrossed by streams, rivers, and valleys. These hills lead upward, gradually forming high plateaus and woodlands and eventually climaxing in spectacular mountain ranges.
As of the mid-1990s, about 37 percent of the country’s area was arable; 17 percent consisted of meadows and pastures; 30 percent was forests and woodlands; and 16 percent was devoted to other uses. Geographers often divide Germany into four distinct topographic regions: the North German Lowland; the Central German Uplands; Southern Germany; and the Alpine Foreland and the Alps.
Area:
total: 357,022 sq km
land: 348,672 sq km
water: 8,350 sq km
Land boundaries:
total: 3,714 km
border countries (9): Austria 801 km, Belgium 133 km, Czech Republic 704 km, Denmark 140 km, France 418 km, Luxembourg 128 km, Netherlands 575 km, Poland 467 km, Switzerland 348 km
Coastline:
2,389 km
Maritime claims:
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: 200-m depth or to the depth of exploitation
Elevation extremes:
lowest point: Neuendorf bei Wilster -3.54 m
highest point: Zugspitze 2,963 m
Natural resources:
coal, lignite, natural gas, iron ore, copper, nickel, uranium, potash, salt, construction materials, timber, arable land
Land use:
agricultural land: 48%
arable land 34.1%; permanent crops 0.6%; permanent pasture 13.3%
forest: 31.8%
other: 20.2% (2011 est.)
Irrigated land:
5,157 sq km (2006)
Total renewable water resources:
154 cu km (2011)
Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):
total: 32.3 cu km/yr (16%/84%/0%)
per capita: 391.4 cu m/yr (2007)
Climate: Cool, continental climate with abundant rainfall and long overcast season. Lower temperatures with considerable snowfall in east and south. Prone to rapid weather variations from merging of Gulf Stream and extreme northeastern climate conditions. More about climate in Germany…
Administrative Division: 16 states (Länder): Baden-Wuerttemberg, Bayern, Berlin, Brandenburg, Bremen, Hamburg, Hessen, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Niedersachsen, Nordrhein-Westfalen, Rheinland-Pfalz, Saarland, Sachsen, Sachsen-Anhalt, Schleswig-Holstein, Thuringia.
Population, Area, and Capitals of the Länder
| State | Capital | Area (km2) | Population (Dec.31,2015) |
| Baden-Württemberg | Stuttgart | 35,752 | 10,879,618 |
| Bavaria | Munich | 70,549 | 12,843,514 |
| Berlin | Berlin | 892 | 3,670,622 |
| Brandenburg | Potsdam | 29,477 | 2,484,826 |
| Bremen | Bremen | 404 | 671,489 |
| Hamburg | Hamburg | 755 | 1,787,408 |
| Hesse | Wiesbaden | 21,115 | 6,176,172 |
| Mecklenburg-Vorpommern | Schwerin | 23,174 | 1,612,362 |
| Lower Saxony | Hanover | 47,618 | 7,926,599 |
| North Rhine-Westphalia | Düsseldorf | 34,043 | 17,865,516 |
| Rhineland-Palatinate | Mainz | 19,847 | 4,052,803 |
| Saarland | Saarbrücken | 2,569 | 995,597 |
| Saxony | Dresden | 18,416 | 4,084,851 |
| Saxony-Anhalt | Magdeburg | 20,445 | 2,245,470 |
| Schleswig-Holstein | Kiel | 15,763 | 2,858,714 |
| Thuringia | Erfurt | 16,172 | 2,170,714 |
Related articles:
Climate In Germany
