September 18, 1630
Death of Melchior Klesl in Vienna, Austria. A Protestant in early life, Klesl converted to Roman Catholicism through the influence of the Jesuits. He became a priest and rose in the church to the office of Bishop of Vienna and finally cardinal. He was close to the Holy Roman Emperor and for a time was in essential control of the Empire. He worked for religious tolerance which offended many of the Catholic princes. He was arrested and imprisoned in 1618. It was not until 1627 that he was able to be released and return as a bishop.
September 18, 1684
Birth of Johann Gottfried Walther in Erfurt, Germany. Walther was a friend of J. S. Bach and also a Baroque composer. His most lasting work, though, was his Musicalisches Lexikon, the first encyclopedia of music. Walther died in Weimar in 1748.
September 18, 1783
 Death of Leonhard Euler in St. Petersburg, Russia (born in Basel, Switzerland). A mathematician of the Berlin Academy, Euler was one of the originators of pure mathematics. He made significant contributions to geometry, calculus, mechanics and number theory as well as observational astronomy. Euler wrote, Introductio in analysin infinitorum (1748), Institutiones calculi differentialis (1755), and calculi integralis (1770) as well as a number of articles in professional journals.
Death of Leonhard Euler in St. Petersburg, Russia (born in Basel, Switzerland). A mathematician of the Berlin Academy, Euler was one of the originators of pure mathematics. He made significant contributions to geometry, calculus, mechanics and number theory as well as observational astronomy. Euler wrote, Introductio in analysin infinitorum (1748), Institutiones calculi differentialis (1755), and calculi integralis (1770) as well as a number of articles in professional journals.
September 18, 1831
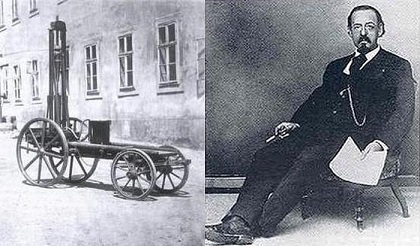 Birth of Siegfried Marcus in Malchin, Germany. Marcus was an inventor who built 4 gasoline-powered automobiles, the first one in 1864, at his workshop in Vienna. After building them, however, he did nothing more with them nor made any attempt to manufacture or sell his inventions. One of his cars still exists and is on display at the Technical Museum for Industry and Trade in Vienna.
Birth of Siegfried Marcus in Malchin, Germany. Marcus was an inventor who built 4 gasoline-powered automobiles, the first one in 1864, at his workshop in Vienna. After building them, however, he did nothing more with them nor made any attempt to manufacture or sell his inventions. One of his cars still exists and is on display at the Technical Museum for Industry and Trade in Vienna.
September 18, 1882
Birth of Bl. Ulrika Franziska Nisch (1882 – 1913) Ulrika Franziska Nisch was born in 1882 in the village of Mittelbiberach-Oberndorf in the state of Württemberg, Germany. She was admitted to the Sisters of the Cross order in 1904. She worked in the kitchen of the order. She reported numerous visions of angels and saints. She was beatified in 1987 by Pope John-Paul II.
September 18, 1972
Death of Robert Faesi in Zollikon, Switzerland. Faesi wrote plays, poetry, short stories and literary criticism. He was a professor of German literature at the University of Zürich. Among his literary works are, Aus der Brandung (1917), Füsilier Wipf (1917), Züricher Idylle (1908) and Die Stadt der Väter, Die Stadt der Freiheit, Die Stadt des Friedens (3 vols. 1941-52). He wrote the libretto for Willy Burkhard’s opera, Die schwarze Spinne. His published correspondence with Thomas Mann appeared in 1962.
September 18, 1973
 East and West Germany are both admitted as full members of the United Nations (UN). The relationship of Germany and the United Nations first began with World War II, with United Nations then being synonymous with the Allies of World War II, and Germany then being the Greater German Reich, a member of the Axis powers. With the war ending in the defeat of Germany, the country’s territory was divided amongst the victors, and what was to remain Germany was under Allied administration. In 1949, two new countries were created in these occupied territories: the Federal Republic of Germany in May, and the German Democratic Republic in October.
East and West Germany are both admitted as full members of the United Nations (UN). The relationship of Germany and the United Nations first began with World War II, with United Nations then being synonymous with the Allies of World War II, and Germany then being the Greater German Reich, a member of the Axis powers. With the war ending in the defeat of Germany, the country’s territory was divided amongst the victors, and what was to remain Germany was under Allied administration. In 1949, two new countries were created in these occupied territories: the Federal Republic of Germany in May, and the German Democratic Republic in October.
The Federal Republic of Germany (West Germany) was admitted to the UN as an observer in 1955. The German Democratic Republic (East Germany) was admitted as an observer in 1972.
September 18, 2005
Federal elections in Germany. Leading Chancellor candidates are Gerhard Schröder and Angela Merkel. Results of the election:
– SPD: 34.3 percent (2002 38.5 percent)
– CDU: 27.8 percent (2002 29.5 percent)
– CSU: 7.4 percent (2002 9.0 percent)
– GRÜNE: 8.1 percent (2002 8.6 percent)
– FDP: 9.8 percent (2002 7.4 percent)
– Die Linke.: 8.7 percent (2002 4.0 percent) and
– Others: 3.9 percent (2002 3.0 percent)







