 The Congress of Vienna (1814-15), convened after Napoleon’s defeat, sought to restore order in Europe disrupted by revolutionary and imperial France. Its members’ objective was a constellation of states and a balance of power that would ensure peace and stability after a quarter-century of revolution and war. In addition to the delegates of many small states, the congress included representatives of five large European states: Austria, Prussia, Russia, Britain, and France. After months of deliberations, the congress established an international political order that was to endure for nearly 100 years and that brought Europe a measure of peace.
The Congress of Vienna (1814-15), convened after Napoleon’s defeat, sought to restore order in Europe disrupted by revolutionary and imperial France. Its members’ objective was a constellation of states and a balance of power that would ensure peace and stability after a quarter-century of revolution and war. In addition to the delegates of many small states, the congress included representatives of five large European states: Austria, Prussia, Russia, Britain, and France. After months of deliberations, the congress established an international political order that was to endure for nearly 100 years and that brought Europe a measure of peace.
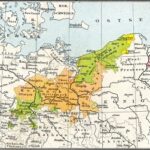
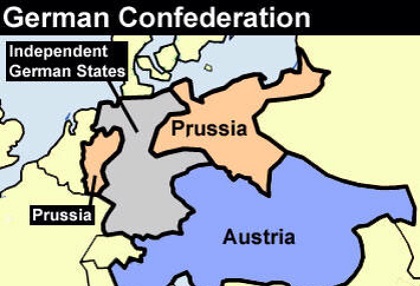
The congress made no effort to restore the Holy Roman Empire and its 300-odd states. Instead, it accepted the disappearance of many small states that had occurred since 1789 and created the German Confederation. The confederation consisted of thirty-eight sovereign states and four free cities and included the five large kingdoms of Austria, Prussia, Saxony, Bavaria, and Wuerttemberg. The confederation met at a diet in Frankfurt, with an Austrian always serving as president.
 Prince Clemens von Metternich, who directed Austria’s foreign policy from 1809 until 1848, was the dominant political figure within the confederation. He waged a decades-long campaign to prevent the spread of revolution in Europe by seeking to restore much of the political and social order that had existed before the French Revolution. Metternich’s Carlsbad Decrees of 1819 established a pervasive system of press censorship and regulation of the universities that dampened German intellectual life and hindered the publication of writings advocating the principles of liberalism. In the 1820s, he engineered the formation of the Holy Alliance of the monarchs of Austria, Prussia, and Russia to quash political, social, and economic developments within Central and Eastern Europe thought to threaten political stability.
Prince Clemens von Metternich, who directed Austria’s foreign policy from 1809 until 1848, was the dominant political figure within the confederation. He waged a decades-long campaign to prevent the spread of revolution in Europe by seeking to restore much of the political and social order that had existed before the French Revolution. Metternich’s Carlsbad Decrees of 1819 established a pervasive system of press censorship and regulation of the universities that dampened German intellectual life and hindered the publication of writings advocating the principles of liberalism. In the 1820s, he engineered the formation of the Holy Alliance of the monarchs of Austria, Prussia, and Russia to quash political, social, and economic developments within Central and Eastern Europe thought to threaten political stability.
Related articles:
Economic and Political Trends in Germany Toward Unification
The Revolutions of 1848
The Restoration of Germany