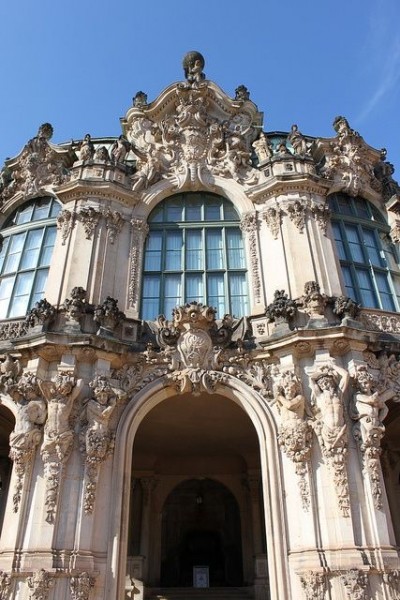
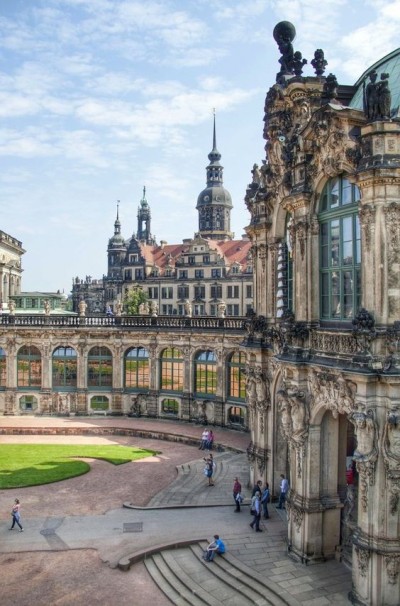
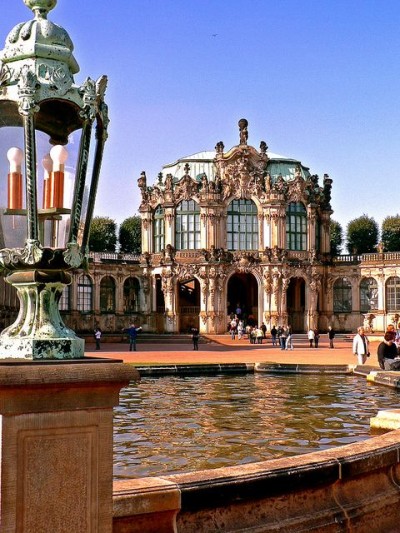
The Zwinger is a palace in the eastern German city of Dresden, built in Rococo style and designed by court architect Matthäus Daniel Pöppelmann. It served as the orangery, exhibition gallery and festival arena of the Dresden Court.
The location was formerly part of the Dresden fortress of which the outer wall is conserved. The name derives from the German word Zwinger (an enclosed killing ground in front of a castle or city gate); it was for the cannons that were placed between the outer wall and the major wall. The Zwinger was not enclosed until the Neoclassical building by Gottfried Semper called the Semper Gallery was built on its northern side.
Today, the Zwinger is a museum complex that contains the Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister (Old Masters Picture Gallery), the Dresden Porcelain Collection (Porzellansammlung) and the Mathematisch-Physikalischer Salon (Royal Cabinet of Mathematical and Physical Instruments).
The Zwinger covers an area on the northwestern edge of the Innere Altstadt (“inner old town”) that is part of the historic heart of Dresden. It is located in the immediate vicinity of other famous sights, including Dresden Palace and the Semperoper opera house.
The Zwinger is bounded by Sophienstraße in the southeast, Postplatz in the south, Ostra-Allee in the southwest, the Am Zwingerteich road in the northwest and Theatre Square (Theaterplatz) in the east. Nearby buildings include the Dresden State Theatre to the southwest, the Haus am Zwinger to the south, the Taschenbergpalais hotel to the southeast, the west wing of the palace with its Green Vault to the east, the Altstädtische Hauptwache to the northeast, the Semper Opera to the north and the former royal stables to the northwest.
The name Zwinger goes back to the common medieval German term for that part of a fortification between the outer and inner defensive walls, or “outer ward”. Archaeological evidence indicates that the construction of the first city wall took place in the last quarter of the 12th century. A documentary entry as civitas in 1216 points to the existence of an enclosed Dresden Fortification at that time. In 1427, during the Hussite Wars, work began on strengthening the city’s defences and they were enhanced by a second – outer – wall. These improvements began near the Wildruffer Tor gate. Step by step the old moat had to be filled in and moved. The area between the two walls was generally referred to as the Zwinger and, in the vicinity of the castle, was utilised by the royal court at Dresden for garden purposes. The location of the so-called Zwingergarten from that period is only imprecisely known to be between the fortifications on the western side of the city.
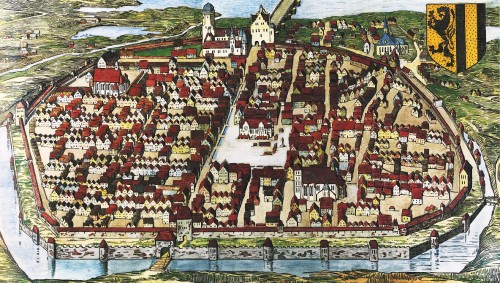
Dresden around 1521 with the course of the nearby Weißeritz river (top left)
This royal Zwingergarten, a garden used to supply the court, still fulfilled one of its functions, as indicated by the name, as a narrow defensive area between the outer and inner defensive walls. This was no longer the case when work on the present-day Zwinger palace began in the early 18th century, nevertheless the name was transferred to the new building. Admittedly the southwestern parts of the building of the baroque Dresden Zwinger including the Kronentor gate stand on parts of the outer curtain wall that are still visible today; but there is no longer any trace of the inner wall.

Zwinger park and memorial photochrome print around 1895
Augustus the Strong, elector of Saxony, returned from a grand tour through France and Italy in 1687–89, just at the moment that Louis XIV moved his court to Versailles. On his return to Dresden, having arranged his election as King of Poland (1697), he wanted something similarly spectacular for himself. The fortifications were no longer needed and provided readily available space for his plans. The original plans, as developed by his court architect Matthäus Daniel Pöppelmann before 1711, covered the space of the present complex of palace and garden, and also included as gardens the space down to the Elbe River, upon which the Semper opera house and its square were built in the nineteenth century.
The Zwinger was designed by Pöppelmann and constructed in stages from 1710 to 1728. Sculpture was provided by Balthasar Permoser. The Zwinger was formally inaugurated in 1719, on the occasion of the electoral prince Frederick August’s marriage to the daughter of the Habsburg emperor, the Archduchess Maria Josepha. At the time, the outer shells of the buildings had already been erected and, with their pavilions and arcaded galleries, formed a striking backdrop to the event. It was not until the completion of their interiors in 1728, however, that they could serve their intended functions as exhibition galleries and library halls.

Nymphenbrunnen in the Zwinger Palace
The building was mostly destroyed by the carpet bombing raids of 13–15 February 1945. The art collection had been previously evacuated, however. Reconstruction, supported by the Soviet military administration, began in 1945; parts of the restored complex were opened to the public in 1951. By 1963 the Zwinger had largely been restored to its pre-war state.













