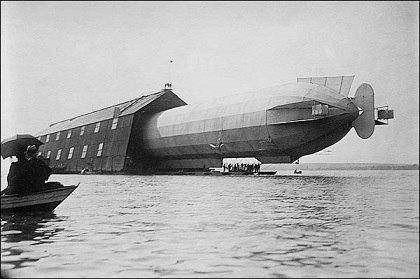
 On July 2, 1900, the first Zeppelin airship took its maiden flight over the Lake Constance near Friedrichshafen. Its creator, Count Ferdinand von Zeppelin, spent two years and all his resources to build the giant – 125 m in length and about 12 m in diameter – cigar-shaped airship equipped with two 14.7 hp Daimler engines. During the construction period, the Count was very often made fun of, and nobody believed that the mammoth creature would ever take off the ground.
On July 2, 1900, the first Zeppelin airship took its maiden flight over the Lake Constance near Friedrichshafen. Its creator, Count Ferdinand von Zeppelin, spent two years and all his resources to build the giant – 125 m in length and about 12 m in diameter – cigar-shaped airship equipped with two 14.7 hp Daimler engines. During the construction period, the Count was very often made fun of, and nobody believed that the mammoth creature would ever take off the ground.
However it happened, though the first flight was not very successful. As the LZ1 (“L” – Luft, the German for “air”, “Z” – Zeppelin) was towed out of its floating hangar and glided marvelously into the sky, something went wrong and after 18 min of flight it splashed down onto the lake and was towed back into the hangar for the fixes and improvements. In about 3 months, in October 1900, the LZ1 was ready to fly again. The airship majestically flew up into the sky, and slowly settled down in the middle of the lake. Which was called an “air train” during the construction, gradually turned into a Zeppelin. Until Count von Zeppelin’s death, 130 Zeppelins were built under his supervision. 96 of them were used in the WWI.
By the beginning of the 20th century the aircraft was quite developed, but this was a very special air ship – it was the first rigid one, having a skeleton built around the bags of lifting gas. The Count von Zeppelin had a few reasons for such a radical design:
– ability of a solid outer shell to allow the airship to travel at much greater speeds without worrying about the air pressure against the nose of the airship;
– real possibility to use the airship for military missions of great duration;
– ability of the aluminum frame to make the airship strong enough to fly through bad weather conditions without deforming itself.
All this was a real danger for the non-rigid ships flown at that time.
During the WWI, Friedrichshafen, where more than a third of all German war planes were produced, became the center of military aviation and arms industry.
Related articles:
The Death of the Hindenburg: The Catastrophe That Ended the Airship Era
How the German Zeppelin Worked: Inside the Engineering of Airship Giants
German Zeppelin: The Rise and Fall of Germany’s Giant Airships
Transportation Future
The Death of the Hindenburg
Zeppelins the Bombers







