Roman Catholicism, one of Germany’s two principal religions, traces its origins there to the eighth-century missionary work of Saint Boniface. In the next centuries, Roman Catholicism made more converts and spread eastward. In the twelfth and thirteenth centuries, the Knights of the Teutonic Order spread German and Roman Catholic influence by force of arms along the southern Baltic Coast and into Russia. In 1517, however, Martin Luther challenged papal authority and what he saw as the commercialization of his faith. In the process, Luther changed the course of European and world history and established the second major faith in Germany–Protestantism.
Roman Catholicism, one of Germany’s two principal religions, traces its origins there to the eighth-century missionary work of Saint Boniface. In the next centuries, Roman Catholicism made more converts and spread eastward. In the twelfth and thirteenth centuries, the Knights of the Teutonic Order spread German and Roman Catholic influence by force of arms along the southern Baltic Coast and into Russia. In 1517, however, Martin Luther challenged papal authority and what he saw as the commercialization of his faith. In the process, Luther changed the course of European and world history and established the second major faith in Germany–Protestantism.
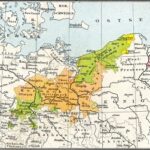
Religious differences played a decisive role in the Thirty Years’ War. An enduring legacy of the Protestant Reformation and this conflict was the division of Germany into fairly distinct regions of religious practice. Roman Catholicism remained the preeminent faith in the southern and western German states, while Protestantism became firmly established in the northeastern and central regions. Pockets of Roman Catholicism existed in Oldenburg in the north and in areas of Hesse. Protestant congregations could be found in north Baden and northeastern Bavaria.
The unification of Germany in 1871 under Prussian leadership led to the strengthening of Protestantism. Otto von Bismarck sought to weaken Roman Catholic influence through an anti-Roman Catholic campaign, the Kulturkampf, in the early 1870s. The Jesuit order was prohibited in Germany, and its members were expelled from the country. In Prussia the “Falk laws,” named for Adalbert Falk, Bismarck’s minister of culture, mandated German citizenship and attendance at German universities for clergymen, state inspection of schools, and state confirmation of parish and episcopal appointments. Although relations between the Roman Catholic Church and the state were subsequently improved through negotiations with the Vatican, the Kulturkampf engendered in Roman Catholics a deep distrust of the empire and enmity toward Prussia.
Prior to World War II, about two-thirds of the German population was Protestant and the remainder Roman Catholic. Bavaria was a Roman Catholic stronghold. Roman Catholics were also well represented in the populations of Baden-Württemberg, the Saarland, and in much of the Rhineland. Elsewhere in Germany, especially in the north and northeast, Protestants were in the majority.
During the Hitler regime, except for individual acts of resistance, the established churches were unable or unwilling to mount a serious challenge to the supremacy of the state. A Nazi, Ludwig Müller, was installed as the Lutheran bishop in Berlin. Although raised a Roman Catholic, Hitler respected only the power and organization of the Roman Catholic Church, not its tenets. In July 1933, shortly after coming to power, the Nazis scored their first diplomatic success by concluding a concordat with the Vatican, regulating church-state relations. In return for keeping the right to maintain denominational schools nationwide, the Vatican assured the Nazis that Roman Catholic clergy would refrain from political activity, that the government would have a say in the choice of bishops, and that changes in diocesan boundaries would be subject to government approval. However, the Nazis soon violated the concordat’s terms, and by the late 1930s almost all denominational schools had been abolished.
Toward the end of 1933, an opposition group under the leadership of Lutheran pastors Martin Niemöller and Dietrich Bonhoeffer formed the “Confessing Church.” The members of this church opposed the takeover of the Lutheran Church by the Nazis. Many of its members were eventually arrested, and some were executed–among them, Bonhoeffer–by the end of World War II.
Religious communities that are of sufficient size and stability and are loyal to the constitution can be recognised as Körperschaften öffentlichen Rechtes (statutory corporations). This gives them certain privileges, for example being able to give religious instruction in state schools (as enshrined in the German constitution, though some states are exempt from this) and having membership fees collected (for a fee) by the German revenue department as “Church tax”: a surcharge of between 8 and 9% of the income tax. The status mainly applies to the Roman Catholic Church, the mainline Protestant EKD, a number of Evangelical Free churches, and Jewish communities. There has been much discussion about allowing other religious groups like Muslims into this system as well.
In the former communist state of East Germany, Christian churches were restricted by the government. In the 21st century Eastern German territories including the capital Berlin is less religious and more secular than Western Germany.
As of 2016, Christianity is the largest religion in Germany, at an estimated 58–59% of the country’s population. The two largest churches of the country are the Roman Catholic Church and the Evangelical Church in Germany (EKD), a Protestant confederation of United Protestant (Lutheran & Reformed), Lutheran, and Reformed churches. Together, both churches claim 55% of the population in 2016, of which 28.5% belonged to the Catholic Church and 26.5% to the Evangelical Church. In 2016, the Orthodox Church constituted 2–2.7% of the population and other minor Christian churches, many of them being Evangelical Protestant, formed 1–1.5%.
About 35–36% of the country’s population are not affiliated with any church or religion, and a minority adhere to other religions. The second largest religion in Germany is Islam, with between 2.1 and 4.7 million adherents (2.6% to 5.7%). Smaller religious groups (less than 1%) include Judaism, Buddhism, and Hinduism.
Related articles:
German Society: Traditions, Modernity, and Cultural Identity
German Society
Structure of German Society
German Population
Women In German Society
Marriage and Family in Germany
Fertility in Germany
Mortality in Germany
Age-Gender Distribution
Population Distribution and Urbanization in Germany
Healthcare in Germany