June 9, 1640 Birth of Leopold I in Vienna. As Emperor of the Holy Roman Empire he brought Austria to a position of influence. June 9, 1775 Birth of Georg Friedrich Grotefend in Münden, Germany. Grotefend made the first major breakthrough in the deciphering of ancient Persian cuneiform script. June 9, 1810 Birth of Otto Nicolai … [Read more...]
German Political Parties
Observers often describe political parties as critical stabilizing institutions in democratic systems of government. Because of the central role played by German political parties, many observers refer to Germany as a "party state." The government of this type of state rests on the principle that competition among parties provides for both popular … [Read more...]
Electoral System of Germany
The Basic Law guarantees the right to vote by secret ballot in direct and free elections to every German citizen eighteen years of age or older. To be eligible to vote, an individual must have resided in a constituency district for at least three months prior to an election. Officials who are popularly elected include Bundestag deputies at the … [Read more...]
Bundesrat of Germany
The second legislative chamber, the Bundesrat, is the federal body in which the sixteen Land governments are directly represented. It exemplifies Germany's federalist system of government. Members of the Bundesrat are not popularly elected but are appointed by their respective Land governments. Members tend to be Land government ministers. The … [Read more...]
German Bundestag
The Bundestag is the principal legislative chamber, roughly analogous to the United States House of Representatives. The Bundestag has grown gradually since its creation, most dramatically with unification and the addition of 144 new representatives from eastern Germany, for a total of 656 deputies in 1990. A further expansion in 1994 increased the … [Read more...]
The Legislature in German Politics
The heart of any parliamentary system of government is the legislature. Germany has a bicameral parliament. The two chambers are the Bundestag (Federal Diet or lower house) and the Bundesrat (Federal Council or upper house). Both chambers can initiate legislation, and most bills must be approved by both chambers, as well as the executive branch, … [Read more...]
The President in Germany
Presidents of the Federal Republic of Germany, 1949- President Years in Office Former Party Affiliation Theodor Heuss 1949-59 FDP Heinrich Lübke 1959-69 CDU Gustav Heinemann 1969-74 SPD Walter Scheel 1974-79 FDP Karl Carstens 1979-84 CDU Richard von Weizsäcker 1984-94 CDU Roman … [Read more...]
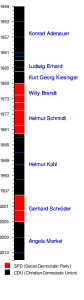
The Chancellor of Germany
The federal government consists of the chancellor and his or her cabinet ministers. As explained above, the Basic Law invests the chancellor with central executive authority. For that reason, some observers refer to the German political system as a "chancellor democracy." The chancellor's authority emanates from the provisions of the Basic Law and … [Read more...]
German Government and Politics
As of mid 1995, Germany was a country coming to terms with the recent unification of its western and eastern portions following four decades of Cold War division. Achieved in October 1990, German unification consisted, in effect, of the incorporation of the German Democratic Republic (GDR, or East Germany) into the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG, … [Read more...]
Culture of German Management
German management, as it has evolved over the centuries and has established itself since World War II, has a distinct style and culture. Like so many things German, it goes back to the medieval guild and merchant tradition, but it also has a sense of the future and of the long term. The German style of competition is rigorous but not ruinous. … [Read more...]
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- …
- 118
- Next Page »