The economic reforms and the new West German system received powerful support from a number of sources: investment funds under the European Recovery Program, more commonly known as the Marshall Plan; the stimulus to German industry provided by the diversion of other Western resources for Korean War production; and the German readiness to work hard … [Read more...]
Bundesbank
The single most important economic institution in Germany outside the federal government is the central bank, the Deutsche Bundesbank (commonly called the Bundesbank). It has the dominant voice in German monetary policy. Through that voice, it establishes and maintains a firm policy in favor of solid currency value within Germany and increasingly … [Read more...]
June 8 in German History
June 8, 1650 Death of Maximilian von Trauttmansdorff in Vienna, Austria. Von trauttmansdorff was an Austrian diplomat who had played a key role in Habsburg imperial politics for many years when he was called upon to negotiate an end to the Thirty Years' War. After negotiations lasting for five years the War ended with the Peace of Westphalia in … [Read more...]
June 7 in German History
June 7, 1826 Death of Joseph von Fraunhofer in Munich, Germany. The physicist, Fraunhofer was the first to observe the dark lines in the spectrum of the sun, which became known as Fraunhofer lines. In his further work he discovered and charted similar spectral lines in the elements. His work led to the development of the technique of … [Read more...]
June 6 in German History
June 6, 1134 Death of St. Norbert von Xanten (ca. 1080 - 1134) St. Norbert was born in about 1080 in Xanten, Germany. He was ordained a priest when he was 35. He gave away all his many properties and dedicated his life to God. In 1119 at the direction of Pope Calixtus II, Norbert founded a religious order at Prémontré (modern France). After … [Read more...]
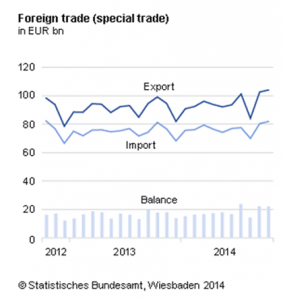
German International Economic Relations
Ever since its creation in 1949, the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG), or West Germany, as it was also called until its unification in 1990 with the German Democratic Republic (GDR, or East Germany), has played an increasingly important role in the world economy. Consistently among the most important trading nations in the world, Germany often … [Read more...]
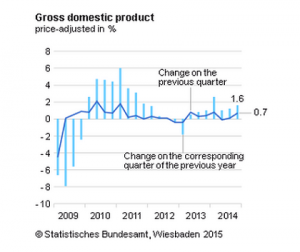
The Domestic Economy of Germany
The German economy is full of contradictions. It is modern but old-fashioned. It is immensely powerful but suffers from serious structural weaknesses. It is subject to national laws and rules but is so closely tied into the European Union that it is no longer truly independent. It has a central bank that controls European monetary policy and has a … [Read more...]
German Economy
The Germans proudly label their economy a "soziale Marktwirtschaft ," or "social market economy," to show that the system as it has developed after World War II has both a material and a social--or human--dimension. They stress the importance of the term "market" because after the Nazi experience they wanted an economy free of state intervention … [Read more...]
Tertiary or Higher Education in Germany
With hundreds of respected universities to choose from as well as its location in the heart of Europe, it’s no wonder that Germany consistently ranks as one of the most popular countries in the world in which to study. There’s Berlin, steeped in history while maintaining a laid-back, trendy feel, and then there is Munich, with its industrial heart … [Read more...]
Vocational Education and Training in Germany
The German education system has been praised for its ability to provide quality general education combined with excellent specific training for a profession or a skilled occupation. In 1992 about 65 percent of the country's workforce had been trained through vocational education. In the same year, 2.3 million young people were enrolled in … [Read more...]
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- …
- 139
- Next Page »